IN-PREP HANDBOOK
Mixed Reality Preparedness Platform (MRPP)
IN-PREP Mixed Reality Preparedness Platform is a user-friendly IT training platform for collaborative response planning. Our platform enables interagency training for the entire chain of command. In a training session, a simulated crisis is created and merged into the real world.
The IN-PREP MRPP
The MRPP provides an interactive visualisation of the crisis environment combining both simulated and real data.
Features include:
- Decision support capabilities with built-in situational awareness
- Resource allocation in real-time
- Rapid remote sensing for quicker response actions
- Large scale evacuation simulation
- Coordinated C2/C3 systems
- Vulnerability and Risk assessment
General Suggestions When using the MRPP
Implementation of cross-organisational training and exercises while using the MRPP:
Preposition:
- The MRPP was designed as a training tool and is not to be confused with a tool to facilitate response operations. At the same time, usually the goal is ‘train as you fight’ and hence it is preferable to train with a tool you would also use in response. These aspects should be taken into consideration when preparing a training or exercise with the MRPP.
- The communication flow of the platform needs to be adapted to the local context specificities. The learning gain of visualising communication flows decreases with the level of cross-organisational collaboration already established in the context of consideration and the respective legacy systems (already) used. In other words, in those cases, in which a respective system is already in place, the added value it more limited than in those cases which operate based on oral (phone/radio) or written (email/white board) communication.
- Use of results: The MRPP encompasses a log function. It should be discussed how decisions are logged and who will own the activities log of the training or exercise.
- Make use of the information and training material to become familiar with the training platform.
Advantages:
- Visualisation/documentation of activities helps to increase mutual understanding; it can be used to revise and or establish SOPs and/or the emergency plans related with the scenario
- The response ratio to certain injects becomes measurable.
- The trainees become more familiar to their plans since they need to interact and document their activities more.
- The MRPP facilitates the development and execution of remote exercises.
Requirements:
- Training should be implemented with the support of a dedicated trainer who is familiar with the MRPP and is able to use its capabilities to a full extent.
- Together with the trainer, the technical set-up needs to be carefully planned. For example: How many monitors will be needed? How many rooms are needed? How can observers be involved?
- From a technical point of view, the MRPP ideally requires two people (trainees) to manage the information flow, one to operate the input to the MRPP and one to watch the information flow on the screen.
- Trainers can pre-prepare injects which ensures their smooth and on-time delivery and thus exercise accuracy. However, it is lacking the option to adapt the scenario very quickly to changing circumstances in the training. Alternative injects would have to be prepared in advance.
- Trainers receive information about the processing of injects. In other words, they are enabled to track whether injects were distributed and received by a certain participant. Hence, trainers can ensure whether messages are actually read, processed and reacted which is difficult when using injects in paper form.
- A scenario archive can be developed which allows for the re-use of scenarios and also the comparison of training response towards similar events. This again facilitates also the comparison of different response strategies and their effectiveness.
- Recommendation engine: Allows for linking the scenario with actions foreseen in the response plans; respective suggestions can be made to the trainee(s).
- Evaluation engine: Allows for the evaluation of use of the use of resources of different organisations.
- The modelling tools are helpful for the development and adaptation of emergency plans. It is recommended to use them in preparation of the exercise. This encompasses particularly the plume modelling and evacuation tools.
- Meta-information about the models, i.e. their data sources and basis for calculating results should be made available to civil protection professionals to allow them to put the results into context.
How to use
The diagram shows the different IN-PREP modules and the relations between the modules. You can find out more information about each module by clicking on a module box. The tabs in the header show the different phases during an exercise. The modules are colour-coded to show which modules should be used during each phase.
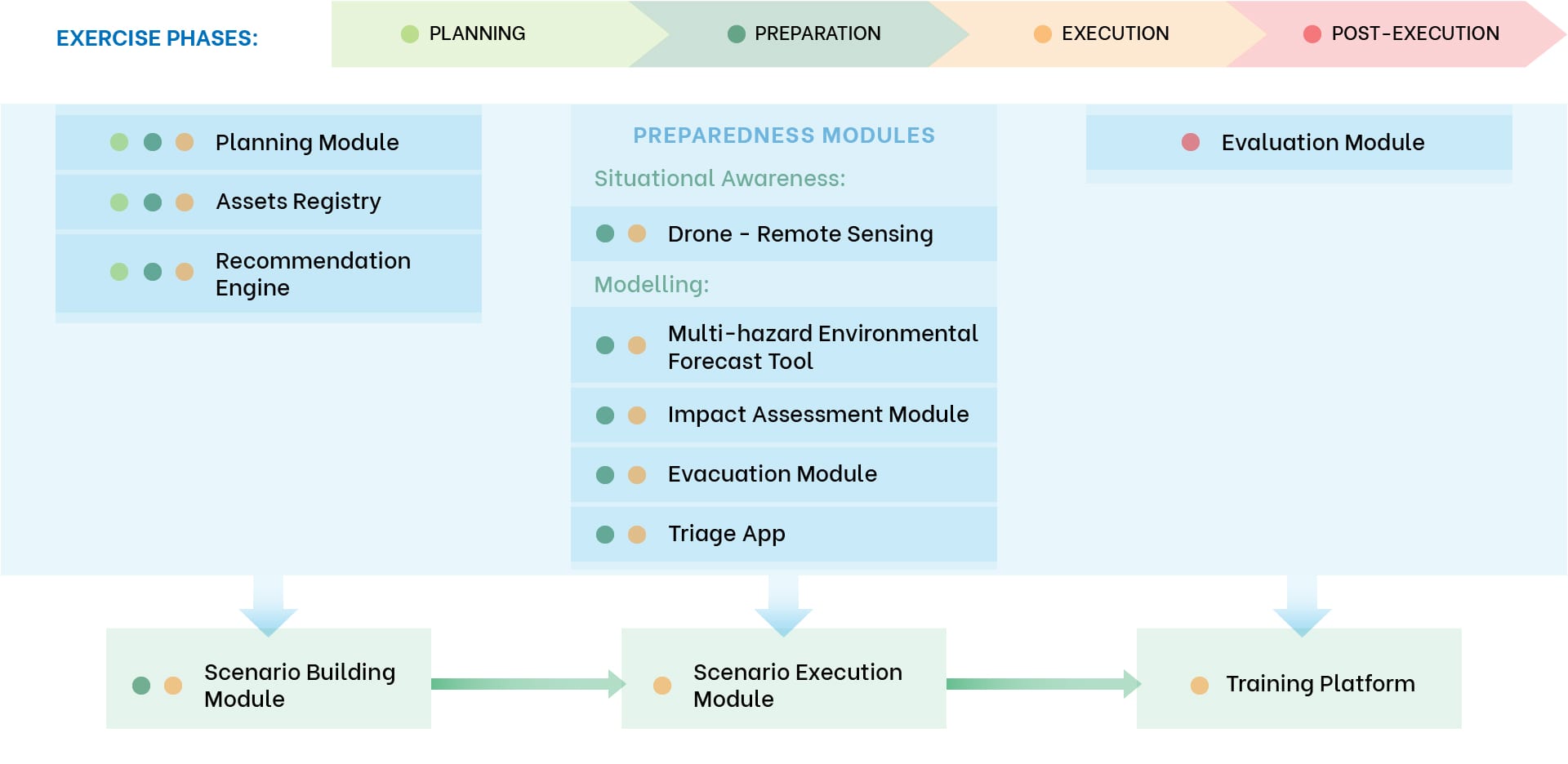
Planning Module
The Planning Module is utilized by the Planner during the planning phase and by the Trainee and Trainer during the exercise execution phase. The Planning Module can be used for creating simple plans (agency-specific, non-collaborative) and save them in the Plans Library, but it can also be used for creating collaborative plans. In the latter case, we name the module Collaborative Planning Module. The Collaborative Planning Module interacts with other planning modules in order to retrieve the simple plans (agency-specific, non-collaborative) and provide them also to the Planner, in order to help them in the creation of collaborative plans.
The IN-PREP Logistics Planning offers a layer that will inform the trainees (at all levels of command and in cross-organisational format) on missions planning, optimisation of transport plan, fleet management and optimisation of the logistics flows, including legal formalities.
Assets registry
The Assets Registry is utilized during
a) The preparation of the exercise, in order for the Exercise Designer to prepare the initial assets (to be used during the execution of the exercise) and
b) During the execution of the exercise, in order for the Trainee to be able to manipulate the assets according to the plan or according to task assignments.
During the exercise preparation the Assets Registry interacts only with the Assets Library. During the execution of the exercise each Assets Registry sends initial and updated information to the Training Module (though the Communication Module) and the Trainee that owns each asset can use the corresponding Assets Registry to manipulate each asset information (e.g. location, status etc.).
The Assets Registry is part of the ENGAGE C2 system.
Recommendation engine
Recommendation Engine is a Decision Support mechanism that collects previous lessons learnt, observations, experts’ opinions and historical data, and uses a set of intelligent algorithms (Fuzzy Logic, Knowledge Graphs and Neural Networks) to unravel correlations with scenario injects, issuing a series of recommendations for trainees across different agencies and command levels.
- Enhance decisions acting as a supportive checklist for trainees
- Issuing different recommendations across different command levels and agencies
- Enhance decision-making skills
- Issuing recommendations based on time-series prediction algorithm (e.g. Flood Level prediction)
- Issuing recommendations based on Social Medial Sentiment Analysis
- Social Media Sentiment Propagation for media crisis preparedness
- Semi-empirical Recommendation based on Knowledge Graphs
- Evacuation Decision based on Neural Networks
- Dynamic Asset Management based on Fuzzy Logic
- Full integrated with Scenario Builder working as one platform
- Integration with Training Platform and C2s through middleware
- Library of historical facts with lessons learned, experts opinion, observations
- Ability to import and export historical facts
- Make the Historical Fact status private or public
End-users are actively involved in the training of the Recommendation Engine, they can monitor algorithms as they are made in ways that let them understand what data is being used, how, and to what end
Each algorithm only covers the context of the OF and ensures that it does not overreach or learn false equivalencies.
Remote sensing (drone)
- Provision of virtual imagery using a drone simulation software and sensor simulation with multiple sensors, or live aerial images and videos with a drone and optical/infrared images and videos.
- Mission requests are received from C2s, a mission is planned and adapted depending on the equipment (drone/camera), and mission status and position is fed back to C2s.
- The setup is flexible and can be adapted to the needs and objectives of the exercise or demonstration.
Crisis managers can receive first sensor data within minutes and act accordingly.
Multiple entities can receive the sensor data at the same time which allows for a quicker assessment based on the same situational picture.
Minimal personnel and other resources are required for the deployment of the sensors and can be used for other collaborative actions.
The response can be planned more precisely and according to the real situation at the crisis area without delay in communication and endangerment of personnel.
No video footage is stored on the drones to support data protection of the public in training and exercises.
Tools to support drone privacy (e.g. https://dronerules.eu/en/) can support users in planning flights in ways that comply with local data protection recommendations.
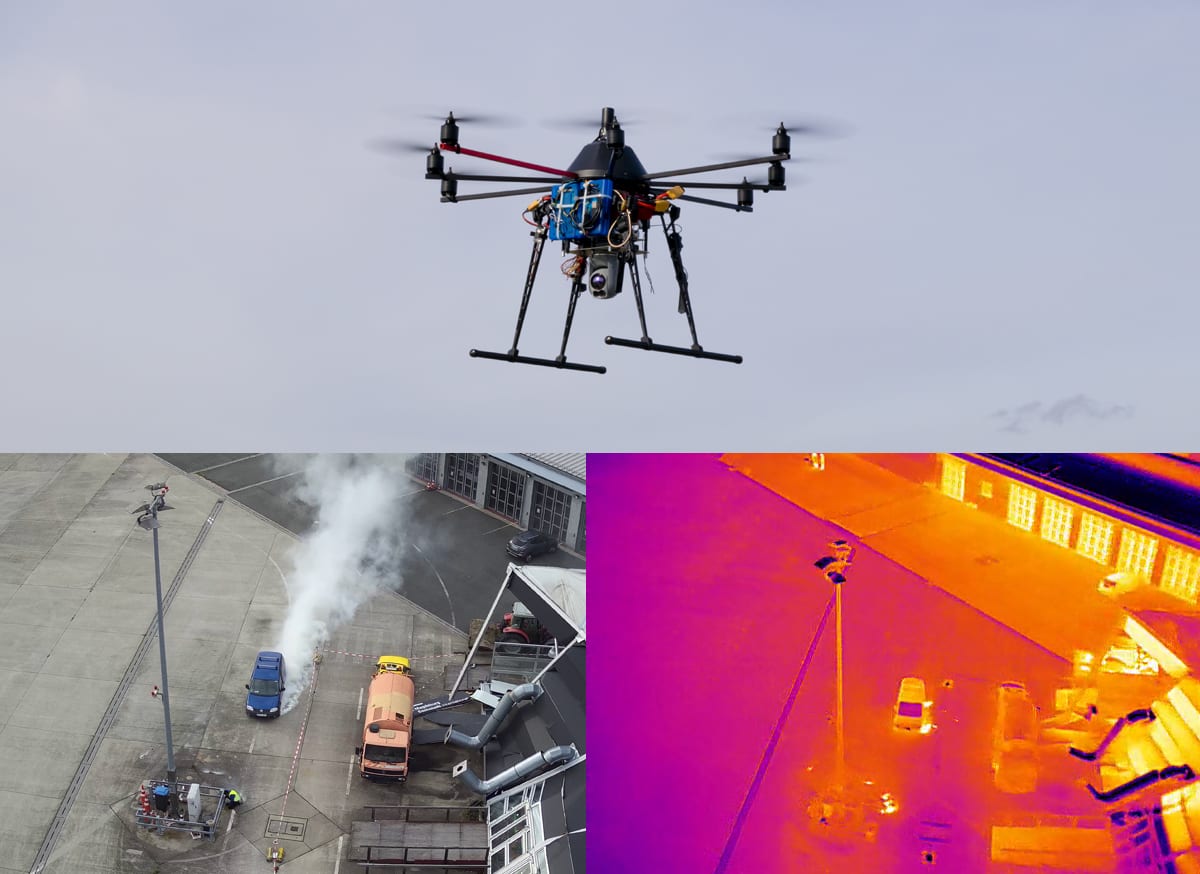

Here is a video explaining the IN-PREP Remote Sensing:
Multi-hazard Environmental Forecast Tool
The IN-PREP Multi Hazard Impact Assessment offers a layer that provides other tools with catastrophe modelling results (disaster functions and assessment needs) based on the specific scenario inputs.
Here is a video explaining the IN-PREP Multi-Hazard Impact Vulnerability Assessment
Impact assessment
- Ability to visualize impact assessment estimates for different natural and man-made hazard scenarios.
- “Impact” is defined in terms of damage and/or economic loss to buildings and/or human casualties (injuries and fatalities).
- Results are displayed in map form on the MRPP interface.
Facilitates the improvement of the user’s situational awareness and ability to take better informed decisions regarding real-time planning, deployment and prioritization of resources to affected areas.
Provides risk and impact results as a range of answers to questions about what could happen were a hazard to unfold, supporting different perspectives on and approaches to risk within a single frame.
The “impact” measures considered within the model are defined in collaboration with end-users to they reflect the most important aspects of how users understand their communities.
The model behind this assessment is built upon an understanding that some sources of data may be affected by bias caused by social and economic factors, thus seeks to address the bias by combining several sources of data about a region.
Evacuation Module
- Provides the capability to simulate pedestrian and vehicle-assisted evacuation scenarios while considering hazard propagation.
- Produces evacuation output data for preparedness and planning that augments information displayed on training and C2 platforms
The Evacuation Module provides insights on evacuation performance by simulating both pedestrian and vehicle evacuation processes. The module is capable of simulating the interactions between pedestrians and vehicles as well as the progressing hazard (wildfire, chemical spill, floodwaters) if such hazard is present in the modelled scenario.
The module produces a plethora of qualitative and quantitative data that highlight elements of the evacuation process including:
- Visual data: depiction of the pedestrian and vehicle movement over the modelled domain and evacuation performance graphs.
- Numerical data: overall evacuation times, time evacuees reached safe locations or target destinations, number of evacuees reaching target destinations, distance travelled, congestion experienced, the impact of hazards on population, number of evacuees being trapped and unable to evacuate.
The use of evacuation simulation allows the users to test and assess the validity of existing evacuation procedures by providing insights on how the evacuation process is likely to unfold. The users can also examine additional what-if scenarios, no matter how unlikely. These tasks are difficult or impossible to examine without the use of simulation tools.
The Evacuation Module is integrated with training and C2 platforms. The data that the module produces is displayed these platforms enabling trainees and crisis managers to better plan for, or to mitigate emergency incidents. This data augments the information displayed on the training and C2 platforms allowing for a fuller understanding of how the incident unfolds and how it can be mitigated allowing for informed decisions to be taken.
It supports descriptive details about individual attributes and vulnerabilities, which can support users in being reflexive and accountable with their assumptions about their local communities.
End-users can actively work with model designers to include relevant population characteristics in their risk management plans and by providing a socio-demographic breakdown of the population of interest to support the model in best representing the local communities for action.
Here is a video explaining the IN-PREP Evacuation Module:
Triage App
A digital bracelet and connected mobile application to support paramedics during triage, collecting relevant data about the triage situation.
Can filter information to other systems, to ensure only relevant information is transferred.
To be used as a training device, volunteer consent and synthetic data can be substituted.
E/PIA:
Designed to be GDPR compliant to support data subject rights.
For data protection, the default settings are for isolated and encrypted data transfer. However, a user can decide to configure them to transfer through a command and control or common information space.
Organisations can develop new digital ethics protocols to support best practices in the field.
Here is a video explaining the IN-PREP Triage Application:
Evaluation Module
The Evaluation Module is utilized
a) During the preparation of the exercise, in order for the Evaluator to prepare the evaluation criteria and evaluation lists,
b) During the execution of the exercise, in order for the Evaluator to fill in the evaluation lists and
c) During the post-execution phase in order for the Evaluator to review the evaluation lists and prepare the evaluation report.
During the preparation of the exercise the Evaluation Module interacts with the Evaluation Criteria Library and the Evaluation Lists Library, facilitating the preparation of the Evaluation Criteria and the Evaluation Lists. During the execution of the exercise the Evaluation Module provide the empty evaluation lists to the Training Module, through the Communication Module. Afterwards the Evaluator uses the Training Module to fill in the evaluation lists and sends them back to the Evaluation Module for storage.
The Evaluation Module is physically integrated into the Training Platform.
Scenario Builder
Scenario Builder provides an intuitive and easy to use way along the appropriate environment for Trainers to abandon scenario-building using pen and paper and instead create in a fast manner draft digital scenarios that can be dynamically edited, modified, executed, re-played and stored. A scenario can be created based on historical or fictitious events, in detail to the second storyline that fully describes a realistic emergency crisis phenomenon. A vast variety of information can be included in each scenario such as actors, assets, events, incidents, events, agency messages, hazard parameters and social media posts. With scenario builder preparedness exercises can be repeated again and again, reducing the overall cost of training while increasing the participation.
- Dynamic scenario creation with adding and editing of injects
- Team drafting capabilities
- Modern UI with a timeline view
- Dynamic creation and editing-on-the-go capabilities of scenario incidents, events
- Detailed to the second scenario with data sources, exchanged messages among agencies and virtual social media posts
- Library of scenarios that can be saved and re-edited again later
- Ability to set scenario status at private or public mode
- Adding and editing scenario actors
- Adding and editing assets (human resources and equipment) on site
- Dynamic Time-plan management
- Run alternative evolutions of the scenario (Easy, Normal, Hard) or sub-scenario
- Scenario Import & Export functionalities
- Team sharing capabilities with access rights management
- Scenario versioning and history tracking
- Integration with Training Platform, C2s and Legacy systems through middleware
It is possible to include injects or models that do not fit expectations and includes categories for scenario elements not always considered by all agencies to encourage new forms of cultural awareness and as bias mitigation.
Watch how to build a scenario on the MRPP
Scenario Execution Module
The Scenario Execution Module is utilized during the execution of the exercise by the Trainer. The trainer initiates the exercise by loading to Scenario Execution Module a predefined (during the exercise preparation phase) scenario script from the Scenario Scripts Library. The Scenario Execution Module interacts with the Training Module, providing it the various information included in the scenario script. The Trainer has the possibility to alter the scenario script during the exercise execution. In this case, the updated scenario script (saved in the Scenario Script Library) is loaded to the Scenario Execution Module.
The Scenario Execution Module is part of the Scenario Building and Execution Tool.
Training platform
- Digital training session management (from the creation to the evaluation)
- Digital collaborative preparedness & planning functionalities
Provides a digital environment for the training.
Information exchanged during the training are being recorded and displayed to the trainer allowing real-time follow-up of the training. Extended evaluation is also possible using recoded data, actions and automatically computed criteria (giving the level of collaboration for instance number of messages exchanged, number of units deployed, …).
The training platform features a Common Operational Picture (COP) sharing geo-localized and consolidated information at the strategic level. Multiple users and agencies can take part in the training physically or remotely sharing information in real-time.
The information displayed to the trainees comes transparently from the scenario, simulation models or other trainees, mixing reality and providing enriched training with situation and data hardly reproducible in regular training.
The training platform features a digital collaborative planning module, allowing the digital plan to be devised from multiple users and agencies. Section of plans can be shared and circulated between agencies to improve the collaborative response.
As a suite, a dedicated common login and authentication system has been designed to ensure GDPR compliance. It also supports controllers in demarcating different access restrictions and access logs.
They are designed multi-layered privacy settings that give the users control over what information is visible, and to whom. For example, a trainee has to opt into having a recording of their training sessions viewed by someone beyond an evaluator.
Proactive engagement with the various disaster risk resource categories and data standards used in these tools can support cross-border or cross-agency collaborators in better understanding each other’s different communication and planning needs.
Working with such platforms for planning and training can help users in identifying features that would be valuable for their collaborative protocols that support users on different sides of the borders better engage with each other’s different approaches to risk.
Use of the system has to come with user-defined protocols and revised duty-of-care for the digital shift. This should include organisational guidance that raises a user’s awareness of when privacy-risking activities could be taking place or where data processing agreements might be needed.


